Cockroaches
Cockroaches are among the most resilient and common pests found in homes and businesses across the United States. Known for their ability to survive in harsh conditions and reproduce quickly, these insects can become more than just a nuisance—they can pose health concerns if left unchecked.
This is your go-to resource for everything you need to know about cockroaches. You’ll learn how to identify the most common species, understand their behavior and preferred hiding spots, discover why they infest certain areas, and find practical tips for preventing and controlling them. Whether you’re dealing with a few sightings or a larger problem, understanding cockroaches is the first step toward keeping your home or business safe and pest-free.
Common Types of Cockroaches in Phoenix
Phoenix’s warm climate makes it an ideal environment for several species of cockroaches. Understanding the most common types can help homeowners identify infestations and take appropriate action:
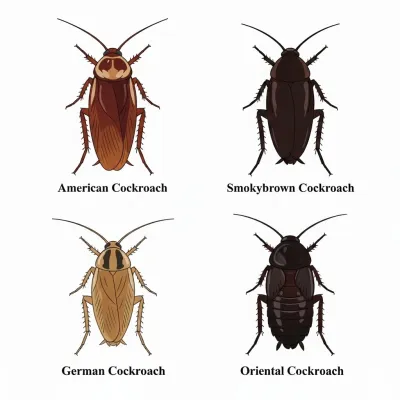
- American Cockroach: Large, reddish-brown roaches that are often found in sewers, basements, and around water sources. They can grow over 2 inches long and are strong flyers.
- German Cockroach: Small, light brown roaches with two dark stripes on their backs. These roaches reproduce quickly and are most often found in kitchens, bathrooms, and areas with food or moisture.
- Smokybrown Cockroach: Dark brown to black roaches that prefer warm, humid areas. They are attracted to outdoor lighting and often enter homes at night.
- Oriental Cockroach: Also called waterbugs, these roaches are dark brown or black and slow-moving. They prefer damp, cool areas such as crawl spaces, drains, and basements.
Most cockroach species in Phoenix are nocturnal, hiding during the day in cracks, crevices, or cluttered areas. Recognizing the species is important for targeting control efforts effectively.
What are the unique characteristics of roaches?
Cockroaches are resilient insects with several features that set them apart from other pests:
- Nocturnal Behavior: Most cockroaches are active at night, hiding during the day in dark, tight spaces such as cracks, behind appliances, and under sinks.
- Fast Reproduction: Cockroaches reproduce rapidly. Female roaches can carry egg cases containing dozens of eggs, which can hatch in just a few weeks under favorable conditions.
- Adaptability: Cockroaches can survive in a wide range of environments, from damp basements to dry kitchens. Some species can even survive without food for weeks and withstand certain harsh conditions that would kill other insects.
- Flat, Flexible Bodies: Their flattened bodies allow them to squeeze through tiny gaps and crevices, making it easy to enter homes and hide in hard-to-reach areas.
- Omnivorous Diet: Cockroaches will eat almost anything, including crumbs, grease, paper, glue, and even decaying matter. This ability helps them thrive in both indoor and outdoor environments.
- Rapid Movement: Cockroaches are quick and can scurry out of sight when disturbed, making infestations difficult to detect early.
- Survival Instincts: Cockroaches can live without air for up to 45 minutes, survive being submerged in water for short periods, and even endure high levels of radiation compared with many other insects.
What Are the Key Traits That Help Cockroaches Survive?
Cockroaches have flat, flexible bodies, fast reflexes, and the ability to adapt to harsh conditions, which makes them incredibly resilient pests in homes and businesses.
Why Are Cockroaches Hard to Detect Early?
Cockroaches hide in dark, tight spaces and are mostly nocturnal. Their small size, quick movements, and secretive habits mean infestations can go unnoticed until populations grow large.
How Do Cockroaches Spread So Quickly?
Rapid reproduction and their omnivorous diet allow cockroaches to thrive almost anywhere. Egg cases can hatch in just a few weeks, and a single female can produce dozens of offspring.
Where are roaches are commonly found?
Cockroaches are highly adaptable and seek out warm, dark, and moist areas where food is available. Some of the most common locations include:
Indoors:
- Kitchens and pantries, especially near crumbs, grease, or spilled food.
- Bathrooms, under sinks, around drains, and behind toilets.
- Laundry rooms, particularly near leaky pipes or damp areas.
- Closets, cabinets, and storage areas with clutter or cardboard.
- Behind appliances like refrigerators, ovens, and dishwashers.
Outdoors:
- Near trash cans, compost bins, and dumpsters.
- Woodpiles, leaf litter, and under rocks or debris.
- Around foundations, vents, and sewer or drainage openings.
- In gardens or shaded, damp areas where insects are plentiful.
Roaches are nocturnal, so you’re more likely to notice signs of activity — like droppings or egg cases — at night. Seeing them during the day often indicates a larger infestation.
What are the risks of having a roach infestation?
Cockroach infestations can pose several risks to homes and families, even if the insects themselves are not venomous:
- Health Risks: Cockroaches carry bacteria, pathogens, and allergens that can contaminate food, surfaces, and kitchen items. Their presence can trigger asthma attacks or allergic reactions, especially in children and sensitive individuals.
- Food Contamination: Roaches scavenge on food, crumbs, and even pet food, leaving droppings, saliva, and shed body parts behind, which can contaminate meals and kitchen areas.
- Rapid Population Growth: Cockroaches reproduce quickly, meaning a small infestation can grow into a major problem in a matter of weeks if not addressed.
- Damage to Property: Roaches can chew on paper, cardboard, fabric, and even electrical wiring, causing damage to stored items, books, and appliances.
- Unpleasant Odors: Large infestations produce a musty, oily odor caused by roach secretions, which can permeate food storage areas, cabinets, and walls.
- Stress and Anxiety: Seeing roaches or signs of their activity can cause stress, discomfort, and fear, especially for homeowners with children or phobias.






